| Contents | Transport layer | Packet format | Application Protocol | Let's write a server |
Application Protocol
As the previous pages have eluded to (you did read them, didn't you?), eAmuse uses HTTP as its main way of getting data around. This means we need an HTTP server running but, as we'll see, we don't need to think too hard about that.
Every request made is a POST request, to //<model>/<module>/<method>,
with its body being encoded data as described in the previous sections. This behaviour can be altered using the
url_slash flag in ea3-config.xml. Disabling this switches to using
/?model=...&module=...&method=... for requests instead. Make sure to implement both of these if
implementing a server!
Every request is followed immediately by a response. Any response code other than 200 is considered
a failure.
Source code details
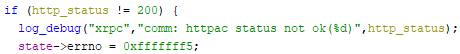
libavs-win32-ea3.dll:0x1000f8e7All requests follow a basic format:
<call model="model" srcid="srcid" tag="tag"> <module method="method" ...attributes> ...children </module> </call>
The responses follow a similar format:
<response fault*="..."> <module status="status" fault*="..." ...attributes> ...children </module> </response>
With "0" being a successful status. Convention is to identify a specific method as
module.method, and we'll be following this convention in this document too. There are
a lot of possible methods, so the majority of this document is a big reference for them all. There are a
number of generic methods, and a number of game specific ones. If you haven't clocked yet, I've been working on
an SDVX 4 build for most of these pages, and each game also comes with its own set of game-specific methods.
These methods are sometimes namespaced tidily, and in other cases are strewn all over the place. Namespaces I'm
currently aware of are listed below. Note that game.* is used by many games, and has identically named
methods within the game module. Expect to need to filter based on model code for this one.
game.* |
Sound Voltex I |
game.sv4_* |
Sound Voltex IV |
game.sv5_* |
Sound Voltex V |
game.sv6_* |
Sound Voltex VI |
exchain_* |
GITADORA EXCHAIN |
matixx_* |
GITADORA Matixx |
nextage_* |
GITADORA NEXTAGE |
op2_* |
Nostalgia Op.2 |
game.*, playerdata.* |
Pop'n Music |
game.* |
HELLO! POP'N MUSIC |
info22.*, player22.* |
Pop'n Music 22 (Lapistoria) |
info23.*, player23.* |
Pop'n Music 23 (éclale) |
info24.*, player24.* |
Pop'n Music 24 (Usagi to Neko to Shounen no Yume) |
game_3.* |
Museca |
info2.*, player2.* |
BeatStream |
Paths in the XML bodies are formatted using an XPath-like syntax. That is, status@/response gets the
status attribute from response, and response/eacoin/sequence would return
that node's value.
NOTE: I am using the non-standard notation of <node* ... and
<node attr*="" ... to indicate that an attribute or node is not always present! Additionally, I
am going to use the notation of <node[]> to indicate that a node repeats.
| Status | Meaning |
0 |
Success |
109 |
No profile |
110 |
Not allowed |
112 |
Card not found (cardmng.inquire) |
116 |
Card pin invalid (cardmng.authpass) |
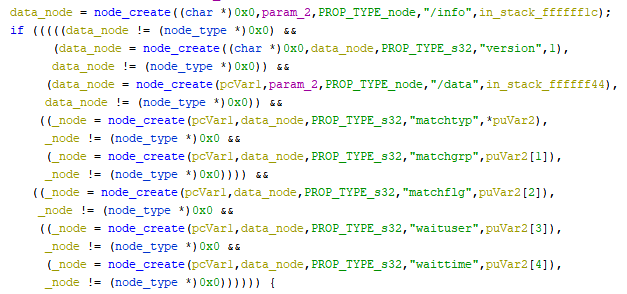
How to reverse engineer these calls
Turns out bemani have been quite sensible in how they implemented their code for creating structures, so it's rather readable. That said, if you've been using Ghidra (like me!), this is the time to switch to IDA. I'll let the below screenshots below speak for themselves:
Ghidra

IDA Pro

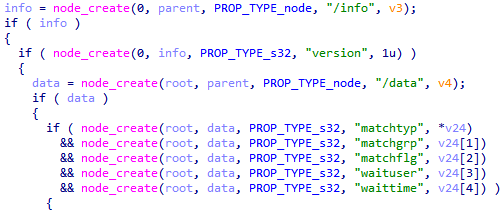
I know which of these I'd rather use for reverse engineering (sorry, Ghidra)!
Service URLs
By design, different modules call to different service endpoints. This is totally optional (all endpoints can be set
to the same value) however it can also be leveraged to simplify deployment. The first request any game makes when
starting is services.get, which is made to the service URL configured in the ea3 configuration. The
response to this request returns a list of endpoints and their corresponding URLs.
Notably, the services.get request contains everything required to identify a game, so it may be
beneficial to route different games to different URLs (where appropriate).
The endpoint names are not the same as module names. Many are, but similarly, many aren't.
| Endpoint | Modules serviced |
lobby |
|
lobby2 |
|
local |
eventlog, game_3 |
local2 |
eventlog, playerdata, matching, system,
esoc, game
|
globby |
|
pkglist |
|
posevent |
|
netlog |
Modules not listed can be assumed to be served by the endpoint of the same name. This table is very incomplete.
Possible XRPC requests
Of which properly documented:
- cardmng
playerdata.%splayerdata.usergamedata_sendplayerdata.usergamedata_recvplayerdata.usergamedata_inheritanceplayerdata.usergamedata_condrecvplayerdata.usergamedata_scorerankmatching.%sservices.%spackage.%seacoin.%seacoin.checkineacoin.checkouteacoin.consumeeacoin.getbalanceeacoin.getecstatuseacoin.toucheacoin.opchpasseacoin.opcheckineacoin.opcheckouteacoin.getlogpcbevent.%spcbtracker.%sapsmanager.%suserdata.%ssystem.%seventlog.%scardmng.%scardmng.inquirecardmng.getrefidcardmng.bindmodelcardmng.bindcardcardmng.authpasscardmng.getkeepspancardmng.getkeepremaincardmng.getdatalistmessage.%sesign.%sdlstatus.%sesoc.%sfacility.%ssidmgr.%straceroute.%sgame.sv4_%sgame.sv4_samplegame.sv4_newgame.sv4_loadgame.sv4_load_mgame.sv4_savegame.sv4_save_mgame.sv4_commongame.sv4_shopgame.sv4_hiscoregame.sv4_buygame.sv4_exceptiongame.sv4_entry_sgame.sv4_entry_egame.sv4_frozengame.sv4_loungegame.sv4_save_egame.sv4_save_pbgame.sv4_save_cgame.sv4_play_sgame.sv4_play_egame.sv4_serialgame.sv4_save_figame.sv4_printgame.sv4_print_hgame.sv4_load_rgame.sv4_save_campaign